Understanding PXE (Preboot Execution Environment)
What is PXE?
Definition: PXE stands for Preboot Execution Environment, an Intel-created technology that enables a PC to boot up using software available over the network. This bypasses the need for local storage devices like hard drives or SSDs.
Functionality: PXE is primarily used to deploy operating systems rapidly across multiple systems, making it an efficient tool in networked environments, such as in enterprises or data centers.
How PXE Works:
Initiation by BIOS: When a computer starts, the BIOS can initiate a PXE boot if configured to seek a network-based boot source before local options.
Network Requirements: PXE requires a network environment configured with DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) servers. These servers direct the PXE-enabled devices to the appropriate boot image.
Process: Upon startup, the BIOS checks for network instructions and interacts with the DHCP server to locate the TFTP server, from which it fetches the boot file to start the operating system installation or load.
Why PXE and Computer Hardware are Discussed Together:
Integration with BIOS/UEFI: PXE functionality is embedded within the BIOS or UEFI firmware of modern computers, enabling them to interact with the network even before the OS loads.
Hardware Dependency: Successful PXE booting depends on compatible network interface cards (NICs) that support PXE standards and are properly configured to communicate with network boot servers.
PXE Use Cases:
Versatile Deployment: Useful for setting up both client and server operating systems without physical media. PXE is particularly advantageous in scenarios requiring rapid provisioning of systems like in server farms or development environments.
Diskless Computers: PXE enables diskless computers to boot up an OS through the network, supporting environments that require high security and centralized management of software resources.
Common Issues and Solutions:
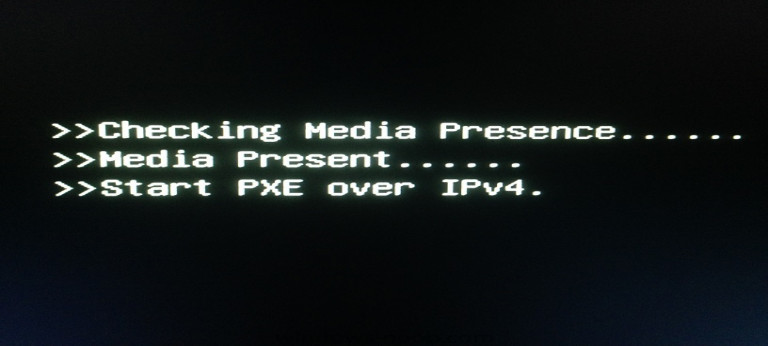
"Start PXE over IPv4" Message: Indicates that the computer is attempting to network boot because it couldn’t find a local boot device. This can happen due to misconfigured BIOS boot order or issues with the local storage device.
Troubleshooting Steps:
Adjust Boot Order: Ensure that BIOS settings prioritize local hard drives over network boot.
Disable Unnecessary Network Boot Options: In BIOS, disable settings like Network Boot or Wake-On-LAN if not required, to prevent unwanted network boot attempts.
BIOS Update: If persistent issues occur, updating the BIOS can resolve compatibility or firmware-related issues affecting boot processes.
Having explored the intricacies of PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) and its crucial role in network-based system booting, it's clear that understanding and managing BIOS settings is pivotal. The initiation of PXE by BIOS, often necessitated by network configurations, leads us to practical steps to ensure systems boot efficiently and correctly. This practical guide starts with the foundational steps to manage your system's BIOS settings—particularly useful when facing common boot issues such as the "Start PXE over IPv4" message. Here’s how you can adjust BIOS settings to rectify boot issues and enhance system startup processes in Windows 11/10:
Method 1: Disable Legacy Support and Secure Boot
Disabling Legacy Support and Secure Boot is essential because these settings can alter your PC's boot order. By adjusting these settings, you can ensure that your PC boots from the correct device.
Steps to Disable Legacy Support and Secure Boot
Access BIOS
Restart your PC and enter the BIOS setup. This is usually achieved by pressing a specific key such as F1, F2, Del, or Esc immediately after turning on the computer.
Modify BIOS Settings
Navigate to the Security tab using your arrow keys.
Locate and select the Secure Boot option, then choose to disable it.
Switch to the Legacy Support option and disable it as well.
Save and Exit
Save your new BIOS settings. Typically, you'll press F10 to save and exit, or you may need to navigate to an 'Exit' menu and select 'Save changes and Exit'.
Exit BIOS. Confirm any prompts to save the settings if asked.
Post-Changes Actions
Addressing the Boot Order Notification
Upon restarting, you might see a notification about a change in the boot order:
If a display number is requested, enter the numbers as instructed (note: these digits won’t be visible as you type).
Confirm your entry and proceed.
Final Steps
If the system boots without requesting a display number, simply allow it to continue.
In cases where further action is needed:
If the system still doesn’t boot correctly, restart and re-enter BIOS.
Go to the Boot tab and ensure the hard drive is set as the primary boot device.
Save and exit BIOS again.
Restart Your PC
Finally, restart your PC to allow the changes to take effect and to see if the issue has been resolved.
Method 2: Disable Wake on LAN
Disabling Wake on LAN is recommended if the first method (disabling Legacy Support and Secure Boot) did not resolve the boot issues. This method is often effective and straightforward.
Steps to Disable Wake on LAN
Preparing to Access BIOS
Shut Down Your PC: Fully power off your computer to prepare for BIOS access.
Click on the Start menu at the bottom left-hand corner of your screen.
Navigate to 'Power' options and select 'Shut Down'.
Entering BIOS
Restart and Enter BIOS:
Turn on your PC and immediately begin pressing the BIOS key to enter setup. Common BIOS keys include F1, F2, F10, Esc, or Del.
You may see a prompt like “Press ... to enter Setup” as the system boots. Act quickly as this message can disappear rapidly.
Locating and Disabling Wake on LAN
Modify BIOS Settings:
Within the BIOS menu, navigate to find the Wake on LAN feature. The location of this setting can vary but is typically found under the 'Power Management' or 'Advanced' tab.
Once you find the Wake on LAN setting, select it and choose the option to disable.
Saving Changes and Exiting
Save and Exit:
Move to the Exit tab within the BIOS setup.
Ensure to save all changes before exiting, typically by selecting 'Save and Exit' or pressing F10.
Confirm any prompts to save the settings and restart the computer.
Ensuring Success
After the PC restarts, observe if the system boots correctly without attempting a network boot via PXE. This change should prevent the system from using Wake on LAN as a boot source, potentially resolving any related startup issues.
Method 3: Upgrade BIOS
Upgrading your PC's BIOS can resolve underlying firmware issues that affect system functionality and compatibility. This process is crucial and requires careful execution due to the risks involved in BIOS updates.
Steps to Upgrade BIOS
Preliminary Checks
Identify BIOS Version:
Access 'System Information' by typing msinfo into the search field at the bottom left-hand corner of your screen, usually found in the Start menu.
Note the 'BIOS Version/Date' listed under the 'Processor' model. Record this information on paper or save it in a document for reference.
Determine System Configuration
Check System Build:
Assess whether your PC was pre-built, bundled, or custom-assembled from various components. This determination is essential to ensure compatibility and prevent issues post-update, as some BIOS updates are specific to certain system configurations.
Prepare for BIOS Update
System Preparation:
If you are updating a laptop, ensure the battery is fully charged. For desktops, connect to an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) to prevent power interruptions during the update process, which could corrupt the BIOS.
Download and Install BIOS Update
Download BIOS File:
Visit your PC manufacturer’s support website and locate the BIOS update files specific to your model. Download the latest version if it is newer than the one currently installed.
Update Process:
Follow the detailed instructions provided by your PC manufacturer, which typically involve running the downloaded executable file or copying it to a USB drive to update the BIOS from within the BIOS setup menu.
Caution and Confirmation
Backup Important Data: Before proceeding with the BIOS update, ensure all important data is backed up as a precaution.
Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Adhere strictly to the guidelines provided by the device manufacturer to minimize risks associated with the BIOS update.
Final Steps
After updating the BIOS, the PC will likely restart automatically. Enter the BIOS setup to confirm that the new BIOS version has been installed successfully.



.png)

